AI-generated TLDR
By performing a quick test—typing “site:yourwebsite.com” into Google—and then setting up Google Search Console, you gain direct, real‑time insights into how Google indexes and evaluates your site. The Console, a free tool from Google, reveals exact data such as search impressions, click‑through rates, and index coverage, letting you spot issues fast. A handy guide from Google walks you through the setup process, while simple checks like running a branded search help you gauge how your brand appears in search results. Together, these steps give you a clear, actionable view of your site’s search performance.
SEO audits often seem intimidating, but after conducting hundreds of them, I’ve discovered a simple truth: we SEO professionals tend to overcomplicate things. This comprehensive guide will walk you through a practical, no-nonsense approach to auditing your website’s SEO performance.
Let’s dive in.
Indexation: Is Google Finding Your Site?
Before diving into advanced tactics, let’s ensure Google can actually see your website. Without proper indexation, all your SEO efforts are essentially invisible.
Quick indexation check:
- Go to Google and type site:yourwebsite.com
- Review the search results
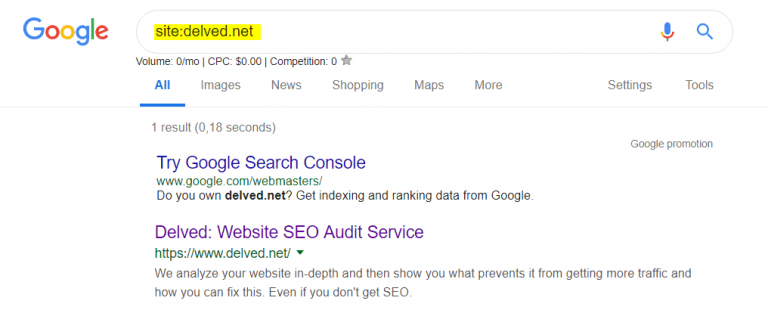
If your website appears in the results, congratulations – Google can index your site. To verify all pages are being indexed, scroll through the results or check specific pages using the same site: command with the full URL.
Crawling: Help Google Navigate Your Website
SEO without proper crawling is like trying to breathe underwater – it simply won’t work. Google’s spiders need to efficiently navigate your site to store it in their index and display it in search results.
For thorough crawl analysis, use Screaming Frog SEO Spider—the free version handles most essential tasks: https://www.screamingfrog.co.uk/seo-spider/
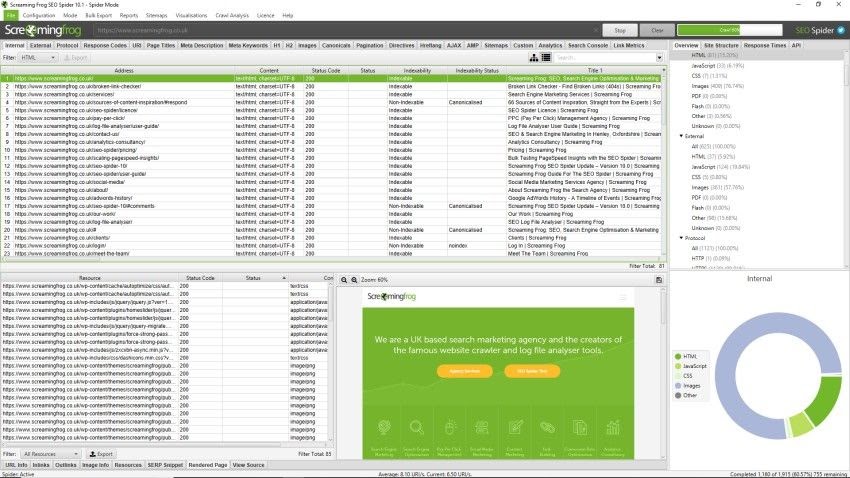
Key elements to analyze during crawling:
Directives – Review canonical tags, noindex/nofollow usage, pagination signals
Title tags – Check for duplicates, missing tags, or length issues
Meta descriptions – Identify duplicates, missing descriptions, or length problems
H1 tags – Ensure each page has exactly one proper H1
H2 tags – Verify appropriate usage throughout content
URIs – Identify overly long URLs, case issues, or problematic parameters
Images – Find missing ALT tags or oversized images
Response codes – Detect redirects, 404s, and server errors
Critical issues to address:
1. Eliminate unnecessary temporary (302) redirects
302 redirects signal temporary changes—use 301s for permanent redirections to preserve link equity and avoid confusion.
2. Fix “not found” (404) errors strategically
Apply this decision framework for 404 pages:
- Pages with traffic and backlinks: Redirect to relevant alternatives
- Pages with no traffic or backlinks: Safe to remove or consolidate
3. Eliminate duplicate elements
Unique page titles, meta descriptions, and heading structures help Google recognize each page’s distinct value and purpose.
4. Add missing essential elements
Ensure every page includes critical SEO elements like titles, meta descriptions, and proper heading hierarchy.
5. Optimize image loading speed
Heavy images significantly impair site performance. Aim to keep image file sizes below 100KB through proper optimization.
Google Cache Check: Confirming Proper Rendering
Verify that Google properly crawls and previews your pages by examining cached versions:
- Search Google for: cache:yourwebsite.com
- Compare the cached version to your live site
The cached version should closely resemble your actual site. This check reveals potential issues with blocked scripts or rendering problems that might prevent Google from properly understanding your content.
Google Search Console: Your Direct Line to Google
Another free tool you should use is Google Search Console
If you’ve never used it before, here’s a gret “how to” guide provided by Google -> click
Google Search Console provides invaluable insights directly from Google itself. If you haven’t set it up yet, follow Google’s official guide: Google Search Console Setup Guide
Essential Google Search Console checks:
- Coverage Report – Review indexing status and identify excluded pages
- URL Inspection Tool – Examine specific URLs for crawling or indexing issues
- Performance Reports – Analyze impressions, clicks, CTR, and ranking positions
The depth of data available in Search Console warrants its own comprehensive guide, but these three areas provide the most immediate value for basic SEO audits.
Site Architecture: Creating an Efficient Structure
A well-structured website benefits both users and search engines by facilitating easy navigation and efficient crawling. Your site architecture affects both user experience and “link juice” distribution.
Key architecture principles:
- Minimize click depth – Every important page should be accessible within 3 clicks from the homepage
- Create logical URL structures – Use clean, shallow URL paths:
Preferred: www.example.com/shoes/nike-44
Avoid: www.example.com/shoes/best-shoes/summer-shoes/nike/nike-44
This principle is particularly crucial for e-commerce sites with thousands of product pages. Remember: pages farther from your most authoritative pages (typically the homepage) generally receive less link equity and indexing priority.
Website Speed: The User Experience Factor
Site speed directly impacts both rankings and user behavior. Studies consistently show that 50% of visitors abandon sites that take more than 2-3 seconds to load, and Google explicitly considers speed as a ranking factor.
Reliable speed testing tools:
- Google PageSpeed Insights/web.dev: https://web.dev
- GTmetrix: https://gtmetrix.com
- WebPageTest: https://www.webpagetest.org (particularly comprehensive)
For accurate assessment, use multiple tools to cross-reference results and implement their recommended optimizations.
They have work to do on that security.Speed optimization checklist:
- Image optimization – Resize and compress all images (try https://squoosh.app)
- Caching implementation – Install plugins like Cache Enabler for WordPress
- Code optimization – Use tools like Autoptimize for WordPress
- Media efficiency – Minimize heavy videos and animations
While perfection isn’t necessary, your site should load in under 3 seconds with a Time to First Byte (TTFB) under 600ms. Most importantly, benchmark against competitors—if they’re faster, you need to prioritize speed improvements.
Mobile Optimization: Google’s Primary Focus
We’re firmly in the mobile-first indexing era, where Google prioritizes the mobile version of your site for crawling and ranking. Testing your mobile readiness is straightforward:
Personally test your site on multiple mobile devices
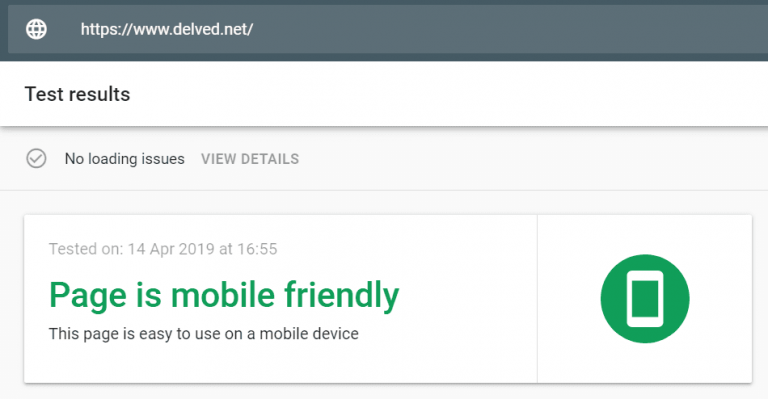
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test: https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly
This is the type of result you want to see. Anything other than this means you need to work on your site to make it mobile friendly. Pro tip: Run the test multiple times for accuracy, and always supplement with actual device testing to ensure intuitive navigation and proper responsiveness.
SSL Security: Non-Negotiable Protection
Encrypted connections are essential for both user privacy and search rankings. Google actively favors secure sites and may penalize those without SSL certificates.
If your URL still begins with http:// instead of https://, implement SSL immediately. Most hosting providers offer free Let’s Encrypt certificates through cPanel, making this a simple fix with significant benefits.
You need to take action to turn it into this:
https://www.example.com## Duplicate Content: Preventing Diluted Authority
Duplicate content issues can severely undermine your SEO efforts by splitting link equity and confusing search engines. Start by checking these common domain variations:
All four versions should redirect to a single preferred version. Also check these technical variations:
- URLs with/without trailing slashes (/)
- URLs with multiple slashes (// or ///)
- URLs with index.html/index.php appended
- URLs with inconsistent case (uppercase/lowercase)
Solutions for duplicate content:
- Implement 301 redirects to canonical versions
- Return 404 errors for incorrect URL variations
- Use proper canonical tags to indicate preferred URLs
Be mindful of repeated content elements across pages, such as headers, footers, and sidebars. While small repetitions aren’t problematic, substantial duplicate content can diminish the unique value of each page.
Content Quality: Addressing Low-Value Pages
Google prioritizes high-quality, valuable content that fulfills user search intent. “Thin” or low-quality pages can drag down your entire site’s perceived value.
Identifying low-value content:
- Systematically review your content and assess whether each page comprehensively addresses its intended purpose
- Compare your content depth against top-ranking competitors for your target keywords
- Identify pages with poor engagement metrics in Analytics
When you discover low-quality pages, either enhance them with substantial improvements or consolidate/remove them entirely. Always prioritize quality over quantity—a few exceptional pages outperform dozens of mediocre ones.
Remember the golden rule: Write for humans first, then optimize for search engines.
Internal Linking: Distributing Page Authority
Strategic internal linking serves three critical functions: facilitating crawling, distributing link equity, and enhancing user navigation. When implemented effectively, internal links amplify the value of your external backlinks by directing their authority to priority pages.
Internal linking best practices:
Ensure links appear natural and helpful to users – avoid excessive linking that appears manipulative
Identify your highest-authority pages (typically those with the most backlinks)
Add relevant internal links from these pages to your priority ranking targets
Backlink Analysis: Evaluating External Authority
Backlinks remain among the most influential ranking factors. Regularly audit your link profile to identify both opportunities and potential problems:
- Use Ahrefs’ free backlink checker: https://ahrefs.com/backlink-checker
- Alternative free tools:https://smallseotools.com/https://monitorbacklinks.com/seo-tools/free-backlink-checker
Remember: sustainable rankings require quality backlinks. Even exceptional content struggles to rank without appropriate external validation through authoritative links.
Technical Fundamentals: Robots.txt and Sitemap.xml
Robots.txt
Search engine spiders first check your robots.txt file for crawling instructions. This file indicates which pages or directories should or shouldn’t be crawled.
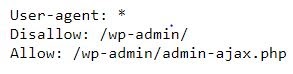
This is what our robots.txt file looks likeFor small to medium websites, a simple setup like the example above is typically sufficient—just ensure the User-agent command is properly configured.
Sitemap.xml
An XML sitemap provides search engines with a complete list of pages you want crawled and indexed. Create and submit your sitemap to all relevant search engines:
- Google: Submit via Google Search Console
- Bing/Yahoo: Submit via Bing Webmaster Tools
- Yandex: Submit via Yandex Webmaster
WordPress users can easily generate sitemaps using the Yoast SEO plugin—simply ensure the XML sitemaps feature is enabled under General > Features.
Consider robots.txt and sitemap.xml as complementary tools that guide search engines through your website efficiently.
Brand Search Performance
Conduct a branded search to evaluate how Google perceives your site. Ideally:
- Your website should rank first for your brand name
- Google should display sitelinks (additional page links) beneath your main result
- Your Google Business Profile should appear (if applicable)
If your site doesn’t rank first for your brand, potential causes include:
- Google penalty affecting site trustworthiness
- Recent site launch with insufficient history/authority
- Exact Match Domain containing common terms
Current Rankings Analysis
Examine your current search positions to establish a performance baseline. Identify both the ranking pages and their corresponding keywords.
For comprehensive data, Ahrefs provides the most robust paid solution. For budget-conscious options, use Google Search Console’s Performance report, which shows queries and pages driving impressions and clicks.
User Experience: The Engagement Factor
Since 2019, user experience metrics have become increasingly influential ranking factors. When users quickly bounce back to search results, Google interprets this as dissatisfaction with your content.
Quick UX analysis framework:
1. Google Analytics metrics
Monitor these critical engagement signals:
- Bounce rate – Should generally stay below 70% for key pages
- Average time on page – Aim for at least 20+ seconds
2. Performance and design evaluation
- Verify site speed from your target audience’s geographic locations
- Assess visual appeal and professional presentation
3. Usability optimization
-
Format content for easy scanning with appropriate spacing, headings, and visual elements
-
Prioritize simplicity and intuitive navigation
-
Conduct user testing with people unfamiliar with your site
-
Ensure prominent visibility of important pages
Competitive Analysis: Benchmarking Performance
SEO is inherently competitive—your rankings depend not just on your own efforts but on how you compare to competitors. A thorough competitive analysis answers these questions:
- Who are your primary organic search competitors?
- What strategies drive their SEO success?
- How strong are their backlink profiles?
- What keywords and positions dominate their visibility?
- Which traffic sources fuel their growth?
Study competitors to identify both successful strategies to adapt and mistakes to avoid—but never simply copy their approach.
Conclusion: Building Your SEO Foundation
An SEO audit establishes the foundation upon which all your optimization efforts will stand. Like constructing a building, you can’t create a stable, high-ranking website without first ensuring its structural integrity.
By systematically addressing each area in this guide, you’ll create a solid platform for sustainable organic growth and improved search visibility.
Notes
- Published: March 9, 2024
- Author: Ves Ivanov
- Source URL: https://vesivanov.com/blog/simple-seo-audit

